Introduction
The beroNet Appliance 2.0 is a telecommunication platform with an Intel Celeron Quad Core processor running a pre-installed beroNet Hypervisor. beroNet customers have the possibility to use the hypervisor to virtualize different operating systems enabling the single system to function as a complete communications hub.
The Appliance can also function as a hybrid device capable of pairing SIP with analog, digital and/or GSM technologies using a beroNet PCIe card.
About the hypervisor
The beroNet hypervisor is based on the XEN Project which is an open source hypervisor that allows multiple operating systems to run concurrently on the same hardware. We decided to implement this open source tool on our device to enhance the possibilities of the beroNet Telephony Appliance.
A. Accessing the hypervisor
Before switching on the appliance, connect it to the network. For this, use the left network card on the appliance. This is necessary so that the DHCP server will provide the system with a local IP address that can be detected by Windows UPnP or thanks to the bfdetect tool. An icon called “beroNet Telephony Appliance” will then appear on another computer connected to the same network under “network devices”.
Then you can login using default credentials of the hypervisor: “admin / beronet”. It is strongly recommended that you change the login credentials for your hypervisor after login.
B. Installing an application from the beroNet market
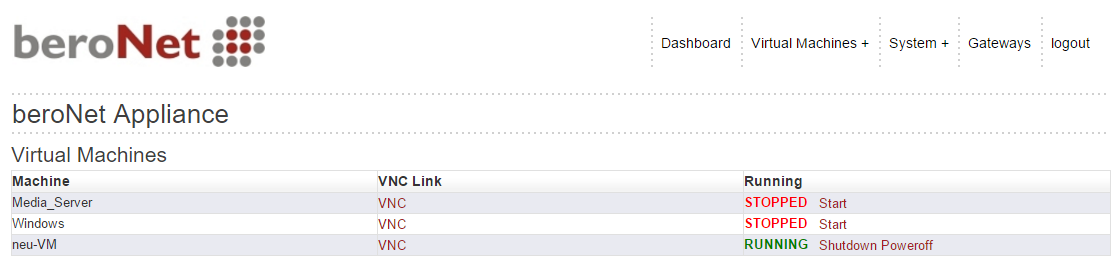
The beroNet market enables integrators to quickly and easily install a new application on the hypervisor. In order to access it, navigate to “market” in the drop down menu under “Virtual Machines+”.
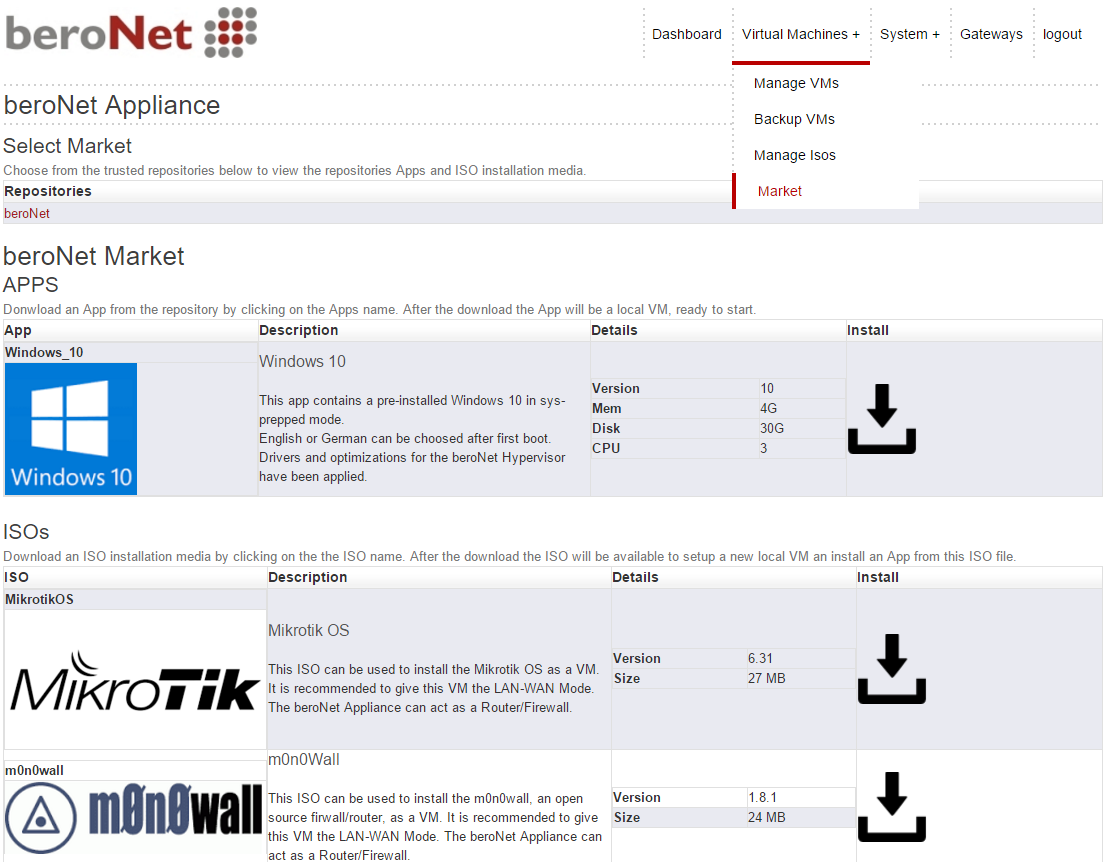
It is then possible to download a complete application from a secure source or only an ISO that will then need to be configured.
The beroNet market is due to evolve thanks to the different technology partners of beroNet, that will make their solutions available on it.
C. Manually install a new virtual machine in the hypervisor
To get started you need to first download an OS (a) and then create a VM(b).
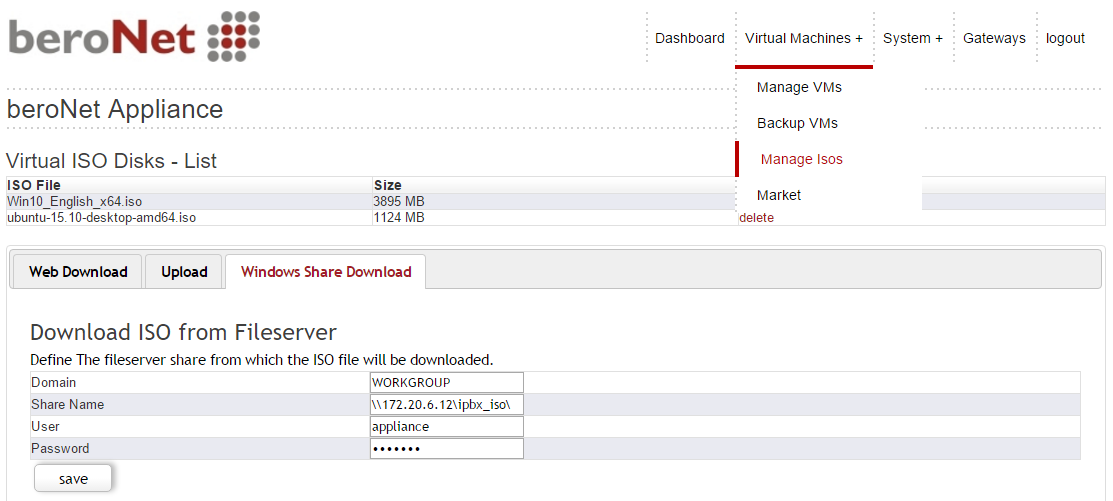
a) Download the ISO from a webserver or from a Fileserver
In order to download an ISO from a webserver, simply enter the URL as below. If needed, add the credentials of the web server using the format: “User:Password”.
It is also possible to upload an ISO from a computer or from a file server. The three options are available under the tab “virtual Machines+” and “manage Isos”:
b) Create a new virtual machine
Under the tab “Virtual Machines+”, it is possible to manage the virtual machines of the hypervisor. In order to create a new one, navigate to the tab “Manage VMs” in the drop down menu.
To create a new VM:
- Give it a name (no spaces);
- Give it one, two or three CPUs;
- Choose how much RAM it should get depending on the size of the appliance (M has 4 GB, L has 8 and XL 16);
- Choose the size of SSD it will be allocated (M has 60 GB, L has 120 and XL 240);
- Choose the ISO file from which the OS has to boot;
- Choose the “Boot-Device”. It should be “d(isofile)” for the installation of the ISO and then “c(disk)” for its use;
- Choose the Network card it will use;
- Give it a “VNC-Display” from 6901 to 6905;
- For a windows installation, add the Windows tools by clicking the box “Windows Tools”.
c) Launch and configure your ISO
Once your OS has been created in the hypervisor, you can easily launch it from the “Dashboard” and start configuring it: